JWT 101: Key to Stateless Authentication
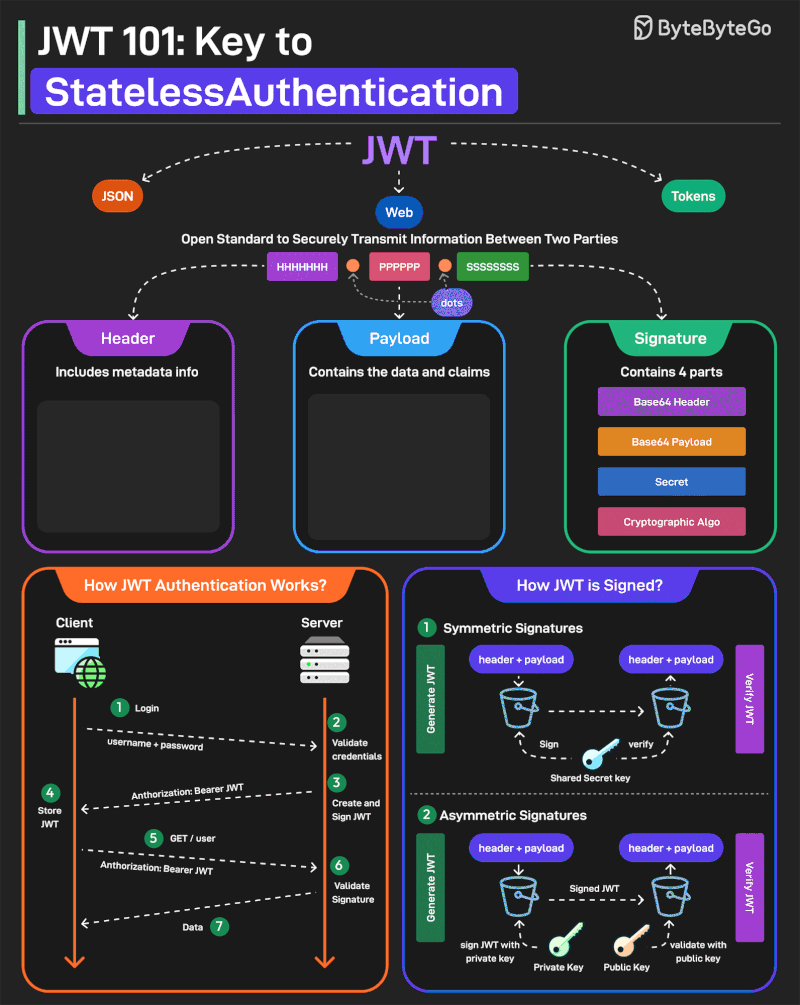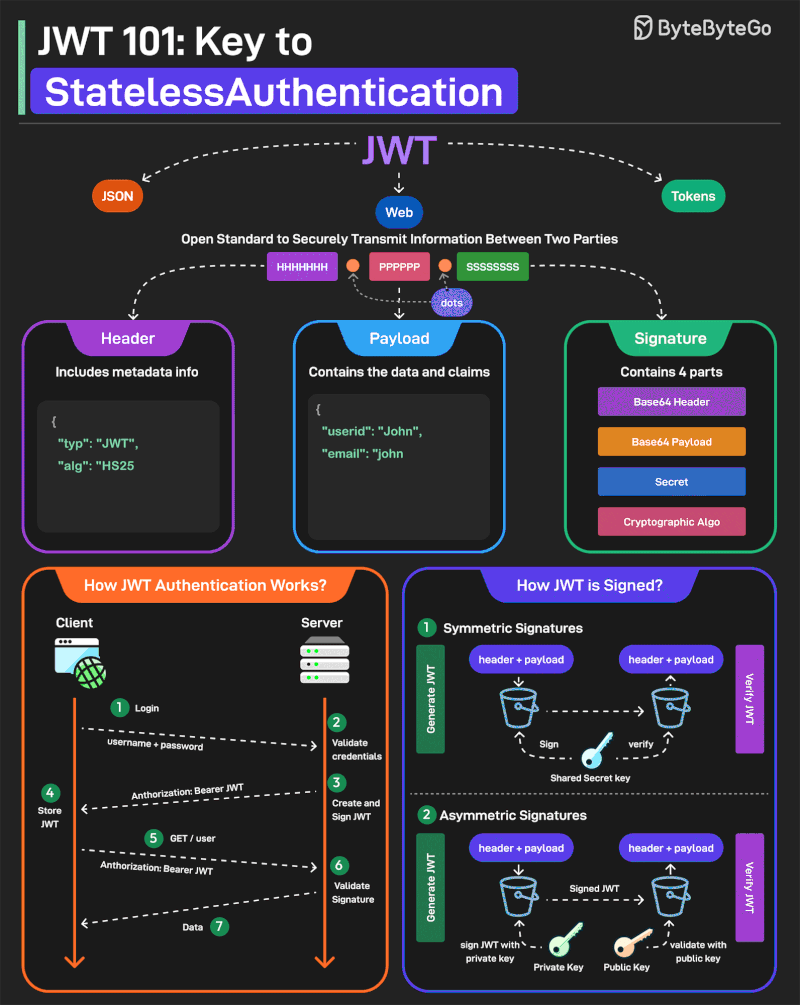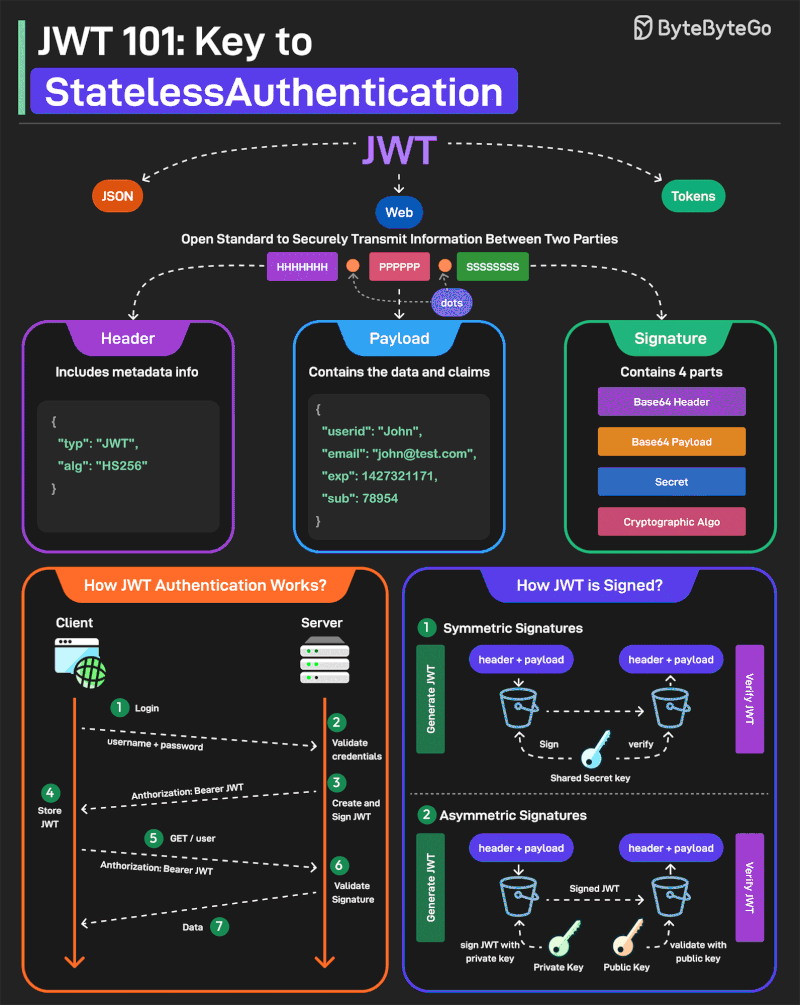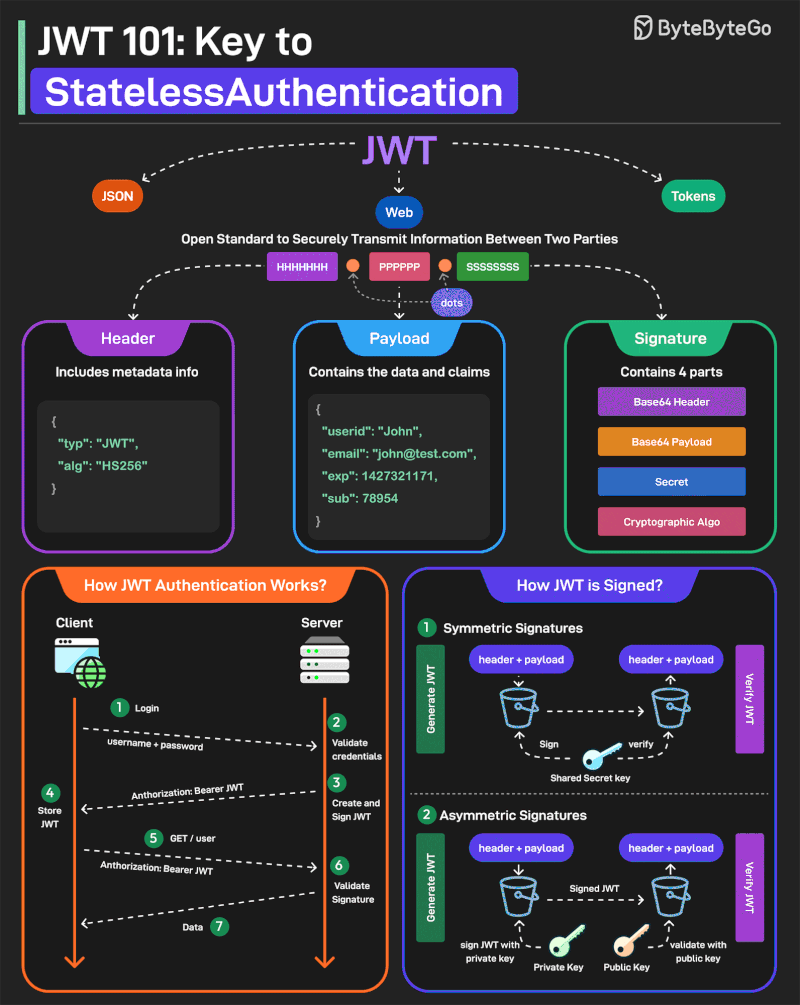
JWT or JSON Web Tokens is an open standard for securely transmitting information between two parties. They are widely used for authentication and authorization.
A JWT consists of three main components:
1 - Header Every JWT carries a header specifying the algorithms for signing the JWT. It’s written in JSON format.
2 - Payload The payload consists of the claims and the user data. There are different types of claims such as registered, public, and private claims.
3 - Signature The signature is what makes the JWT secure. It is created by taking the encoded header, encoded payload, secret key, and the algorithm and signing it.
JWTs can be signed in two different ways:
1 - Symmetric Signatures It uses a single secret key for both signing the token and verifying it. The same key must be shared between the server that signs the JWT and the system that verifies it.
2 - Asymmetric Signatures In this case, a private key is used to sign the token, and a public key to verify it. The private key is kept secure on the server, while the public key can be distributed to anyone who needs to verify the token.