How Digital Signatures Work?
A digital signature is a specific kind of electronic signature to sign and secure electronically transmitted documents.
Digital signatures are similar to physical signatures since they are unique to every person. They identify the identity of the signer.
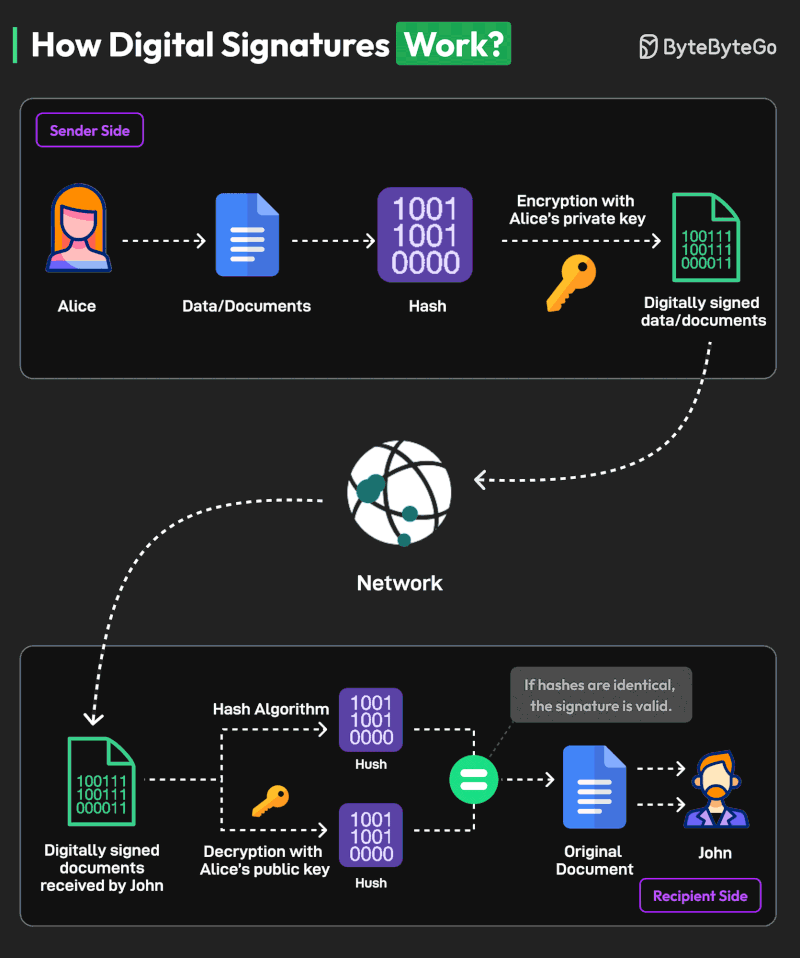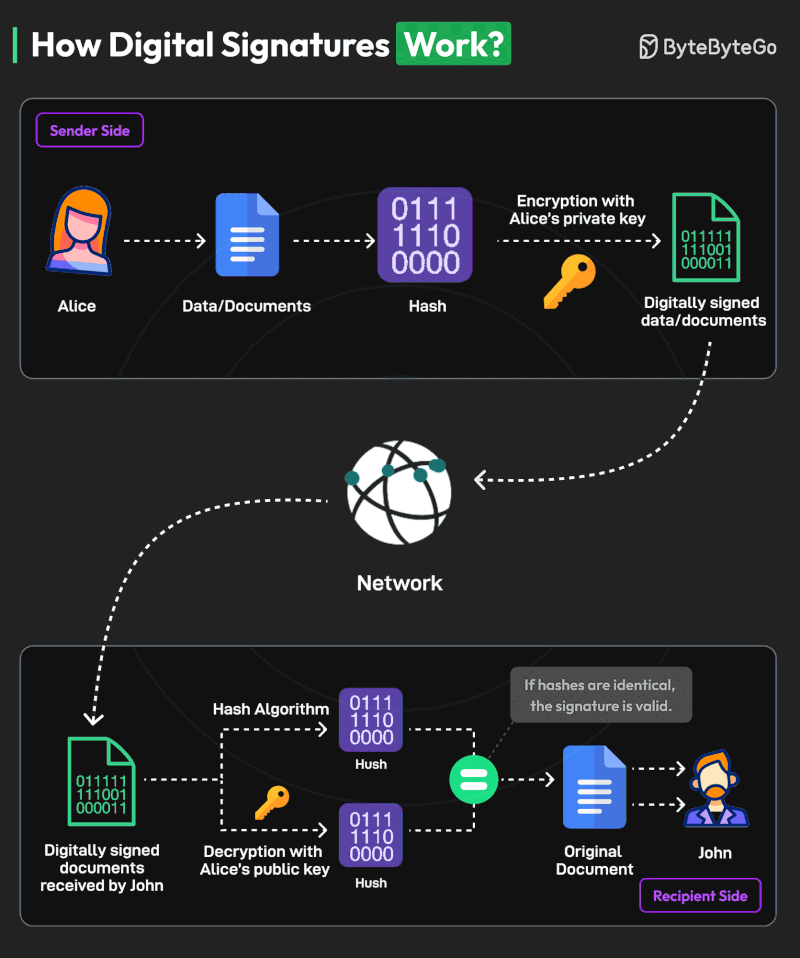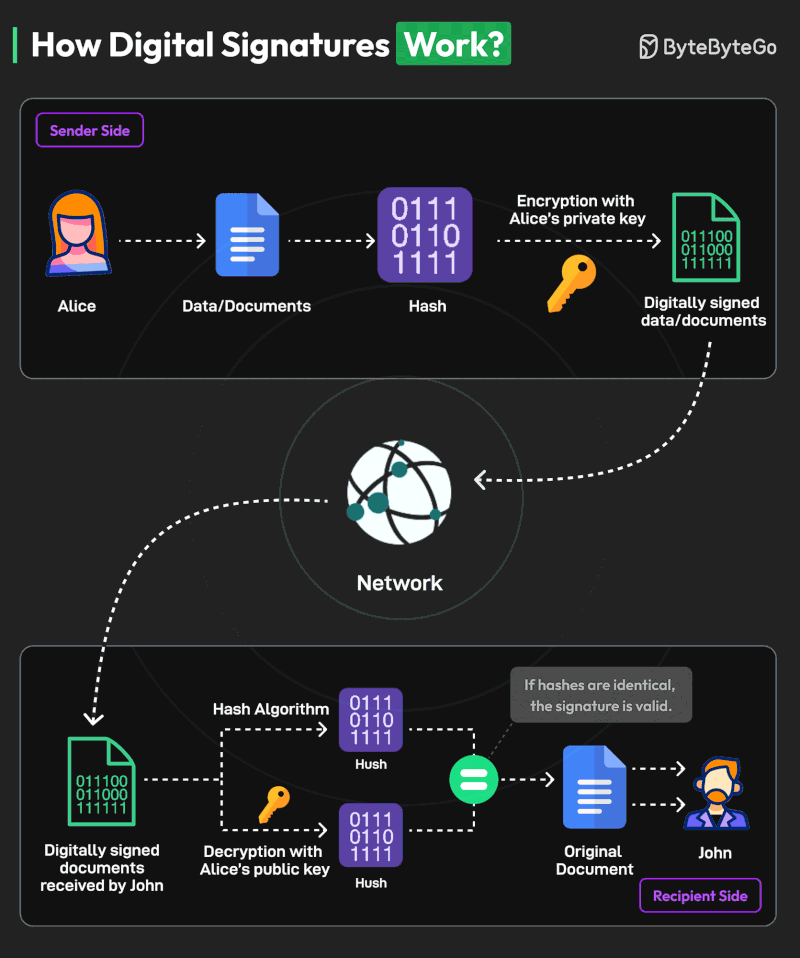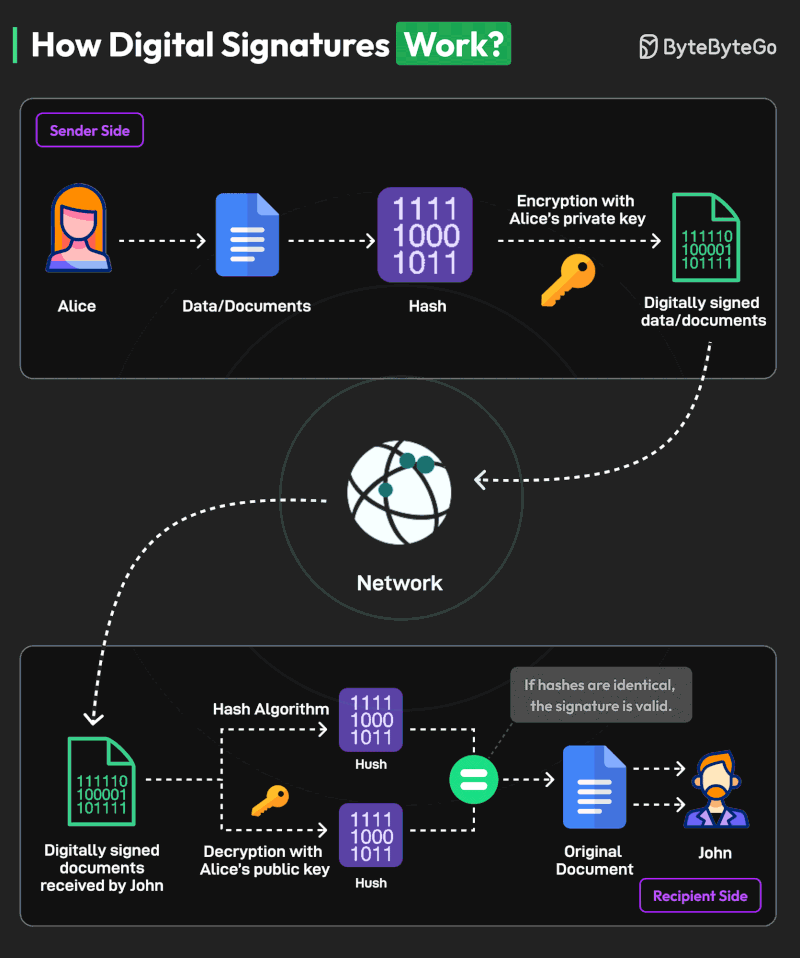
Here’s an example of the working process of a digital signature with Alice as the sender and John as the recipient:
- Alice generates a cryptographic key pair consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key. The private key remains confidential and is known only to the signer, while the public key can be shared openly.
- The signer (Alice) uses a hash function to create a unique fixed-length string of numbers and letters, called a hash, from the document. This hash value represents the contents of the document.
- Alice uses their private key to encrypt the hash value of the message. This hash value is known as the digital signature.
- The digital signature is attached to the original document, creating a digitally signed document. It is transmitted over the network to the recipient.
- The recipient (John) extracts both the digital signature and the original hash value from the document.
- The recipient uses Alice’s public key to decrypt the digital signature. This produces a hash value that was originally encrypted with the private key.
- The recipient calculates a new hash value for the received message using the same hashing algorithm as the signer. They then compare this recalculated hash with the decrypted hash value obtained from the digital signature.
- If the hash values are equal, the digital signature is valid, and it is determined that the document has not been tampered with or altered.