Linux Boot Process Illustrated
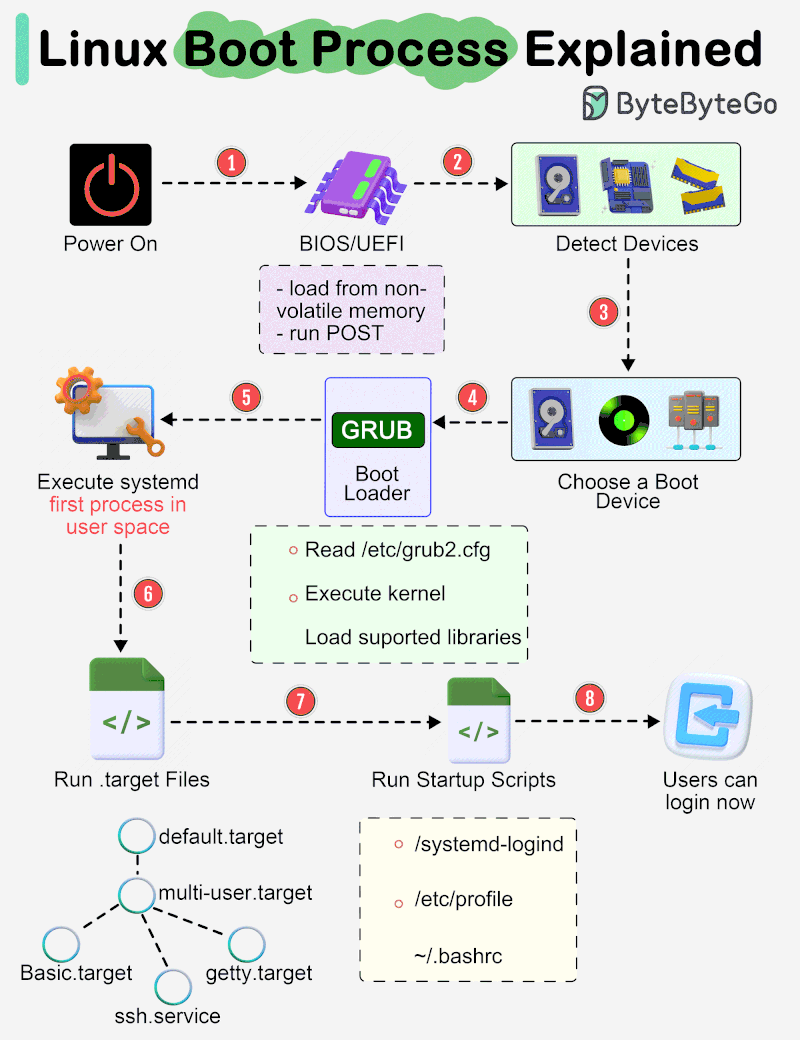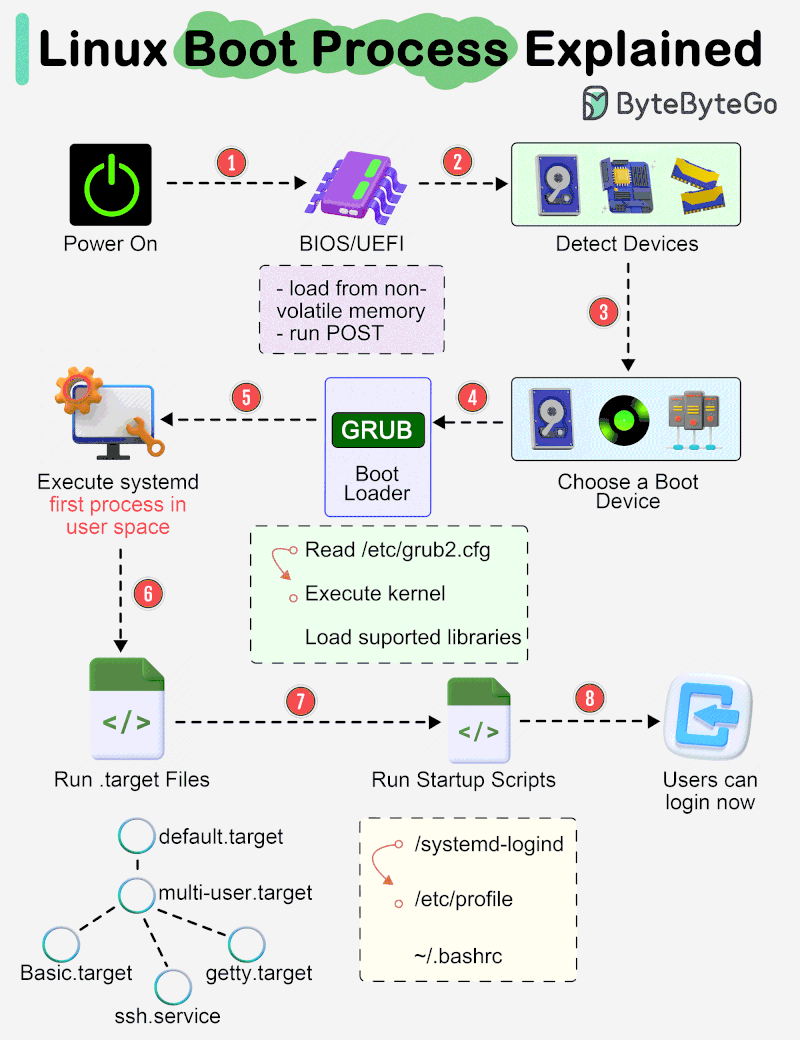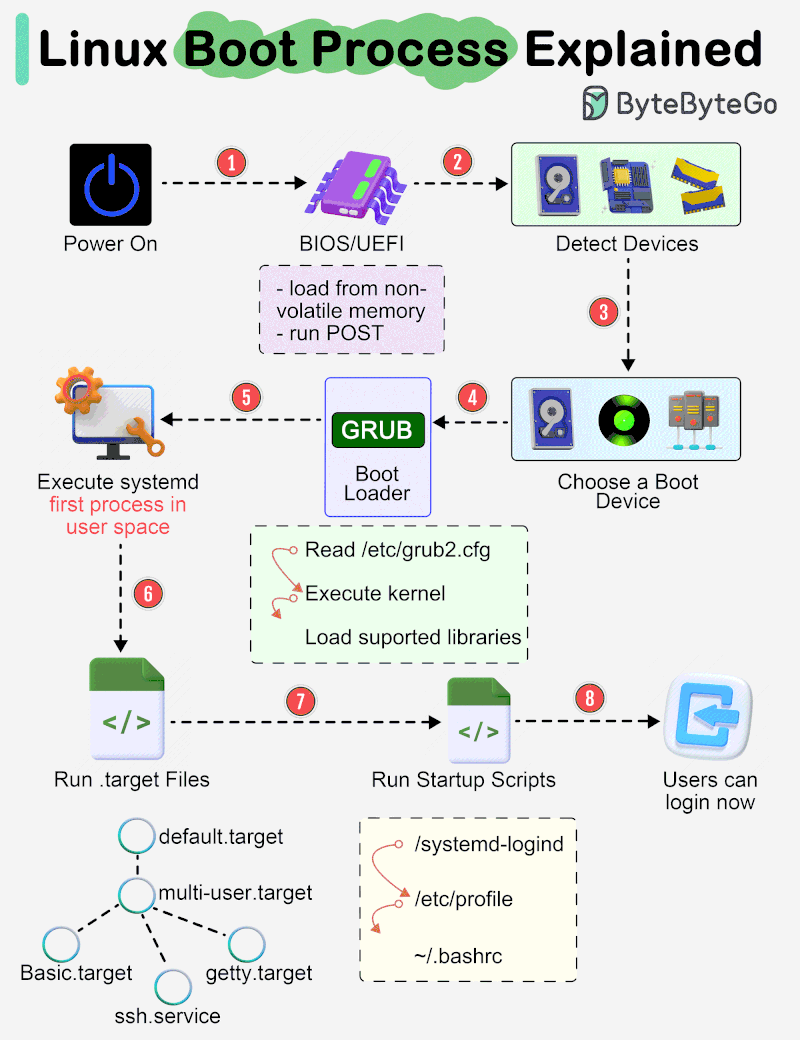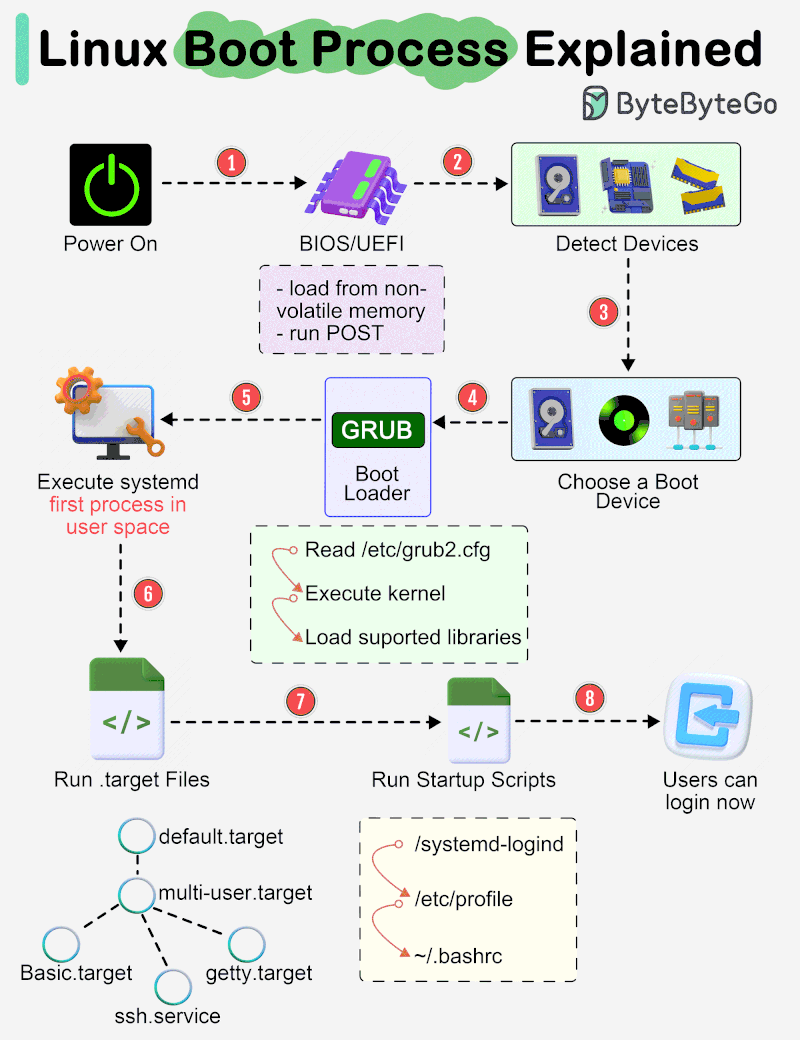
The diagram below shows the steps.
Step 1 - When we turn on the power, BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) firmware is loaded from non-volatile memory, and executes POST (Power On Self Test).
Step 2 - BIOS/UEFI detects the devices connected to the system, including CPU, RAM, and storage.
Step 3 - Choose a booting device to boot the OS from. This can be the hard drive, the network server, or CD ROM.
Step 4 - BIOS/UEFI runs the boot loader (GRUB), which provides a menu to choose the OS or the kernel functions.
Step 5 - After the kernel is ready, we now switch to the user space. The kernel starts up systemd as the first user-space process, which manages the processes and services, probes all remaining hardware, mounts filesystems, and runs a desktop environment.
Step 6 - systemd activates the default. target unit by default when the system boots. Other analysis units are executed as well.
Step 7 - The system runs a set of startup scripts and configure the environment.
Step 8 - The users are presented with a login window. The system is now ready.