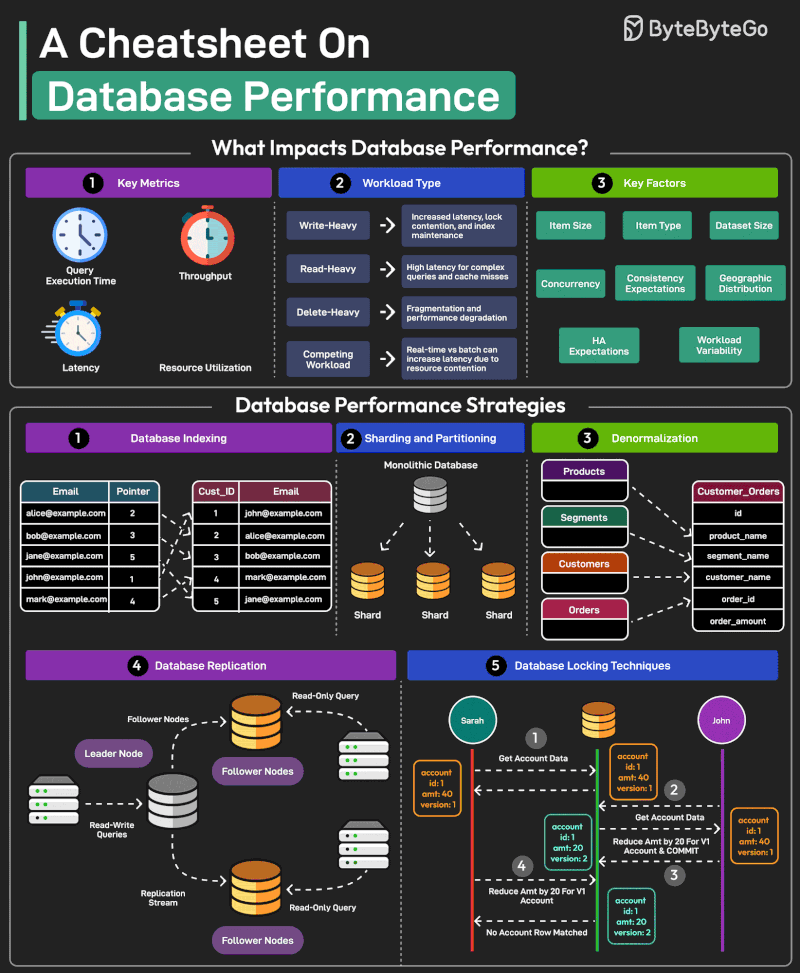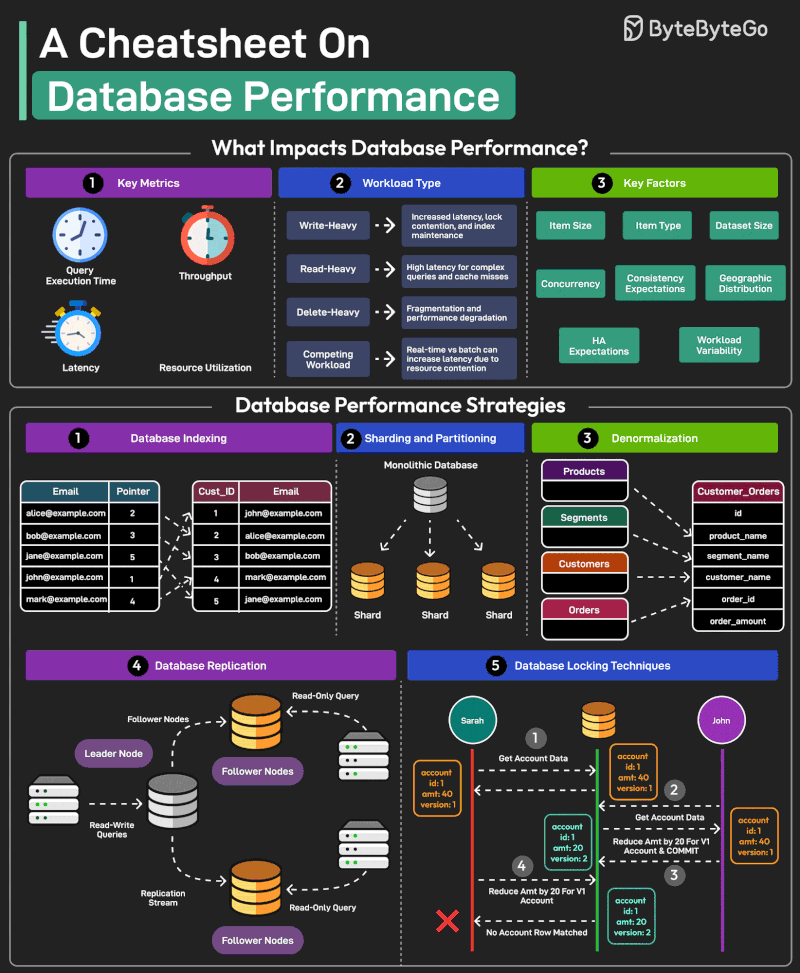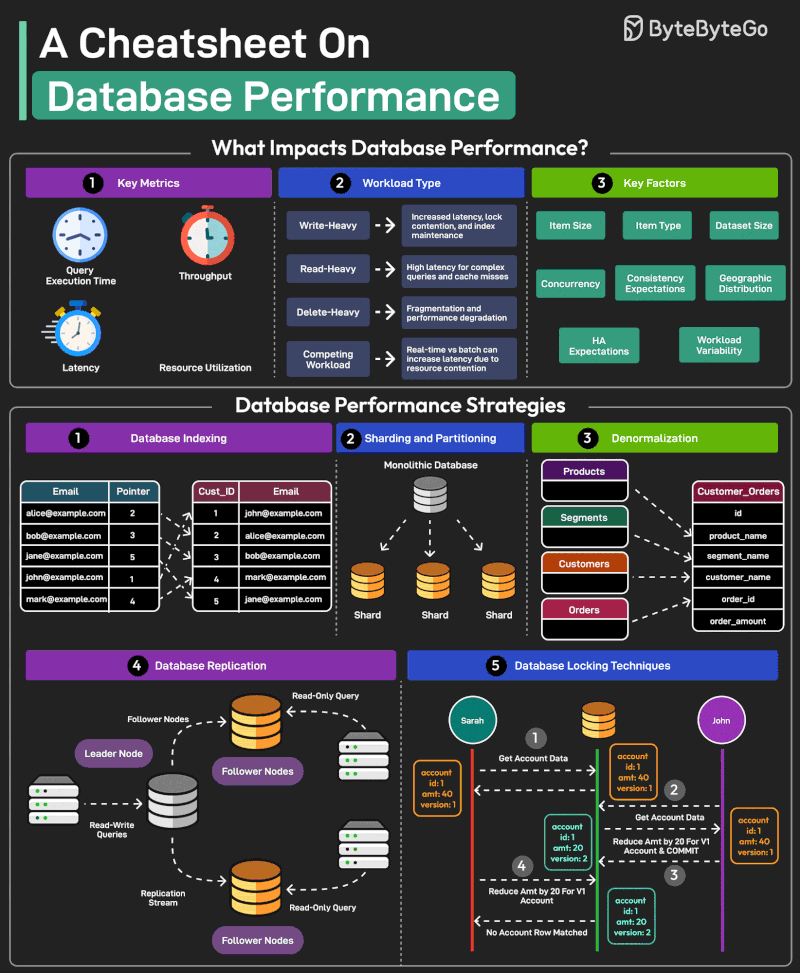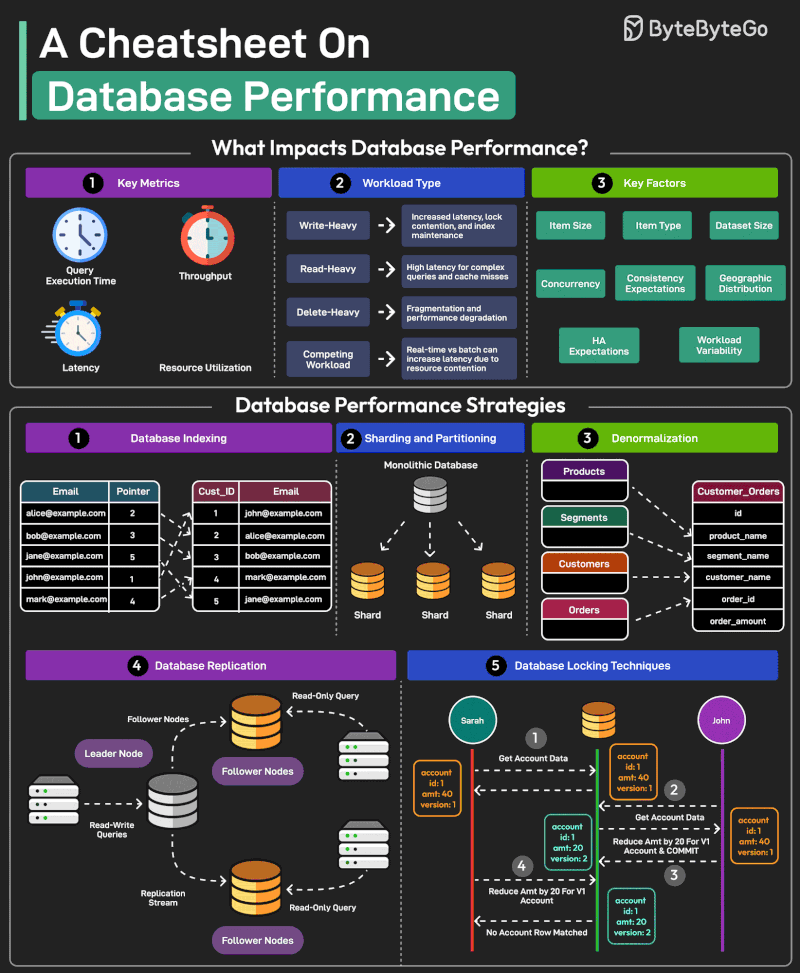
Good database performance is critical since it directly impacts user experience, operational costs, and scalability.
But what impacts database performance?
- Evaluating database performance depends on key metrics such as query execution time, throughput, latency, and resource utilization. - Workload Types such as write-heavy, read-heavy, delete-heavy, and competing workloads pose unique challenges. - Other factors that impact performance are item size, item type, dataset size, concurrency expectations, consistency requirements, HA expectations, and geographic distribution.
Multiple strategies exist to improve database performance. Some of the most important ones are as follows:
1 - Database Indexing Indexes are important for speeding up database queries by reducing the amount of data scanned. Also, choosing the right index type is crucial.
2 - Sharding and Partitioning Divide the data into smaller, more manageable chunks known as shards. Each shard is also stored on a different server.
3 - Denormalization Denormalization combines data into fewer tables to reduce the overhead of joins, improving read performance.
4 - Database Replication Replication involves maintaining multiple copies of the same database, typically with a primary node for writes (and critical reads) and secondary nodes for most read operations.
5 - Database Locking Techniques Use locking techniques like pessimistic and optimistic locking to manage concurrency levels and resource contention.