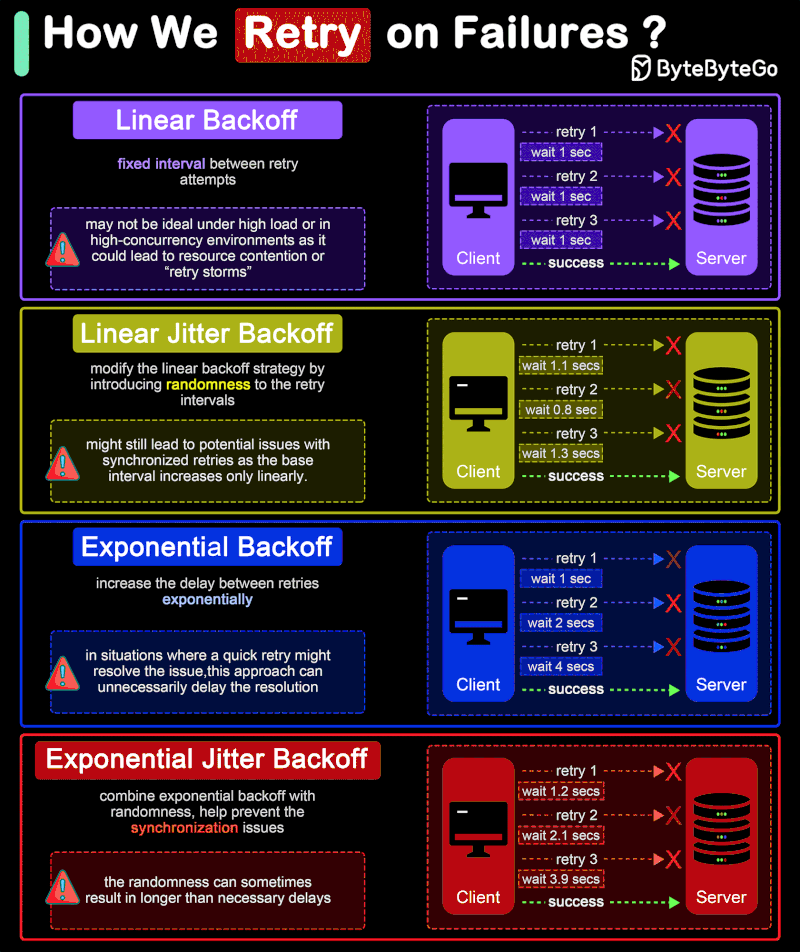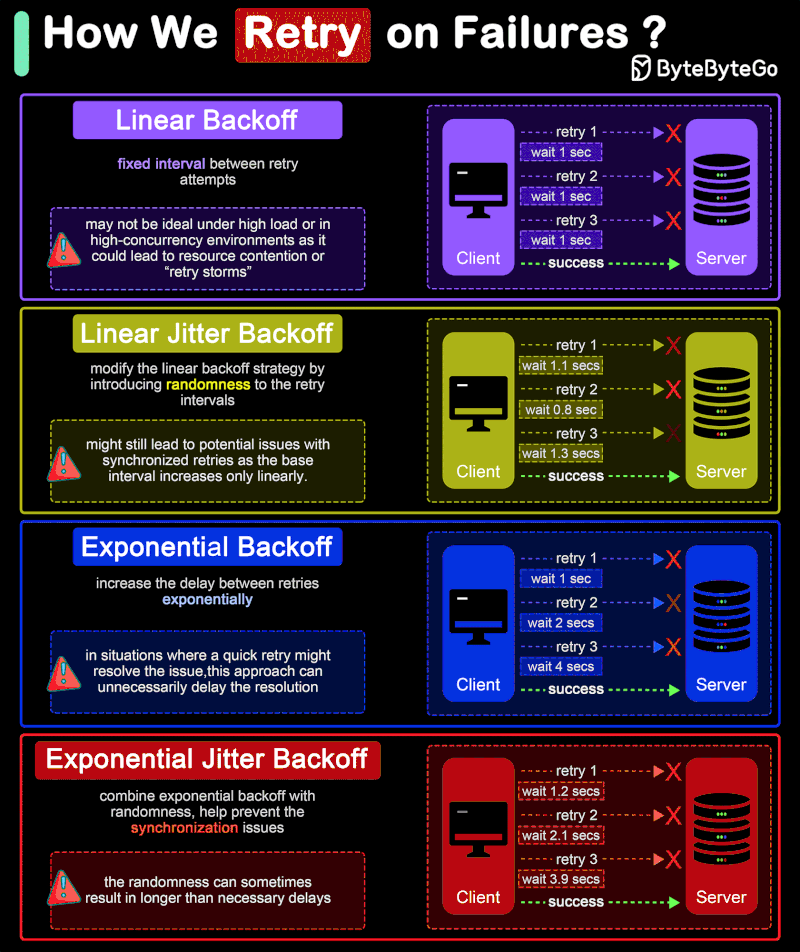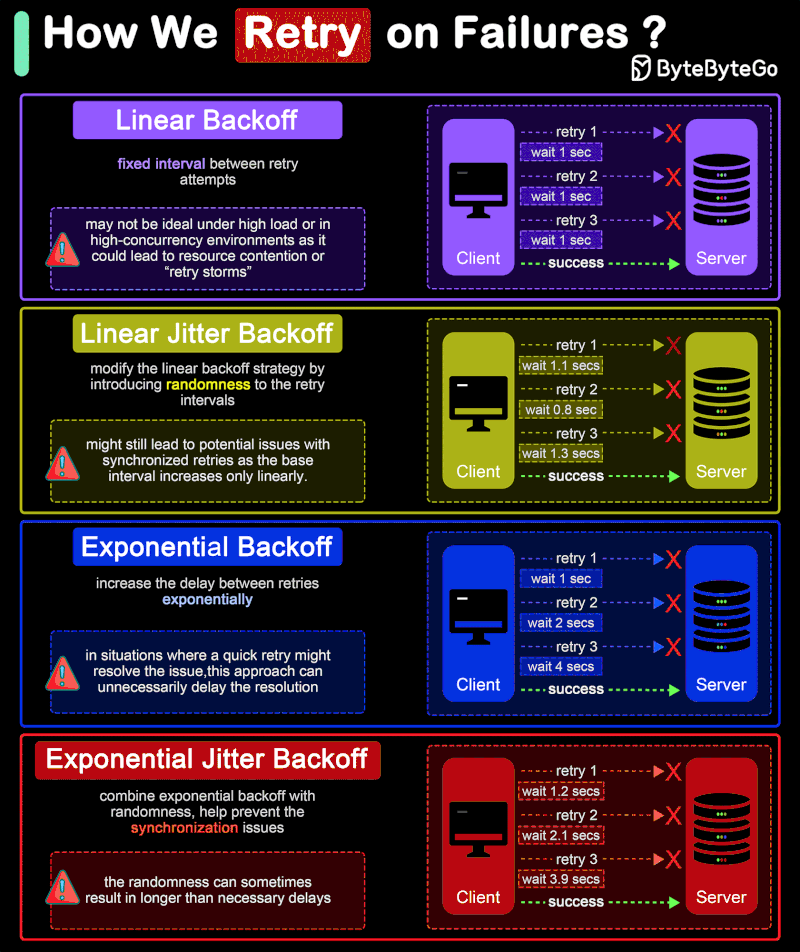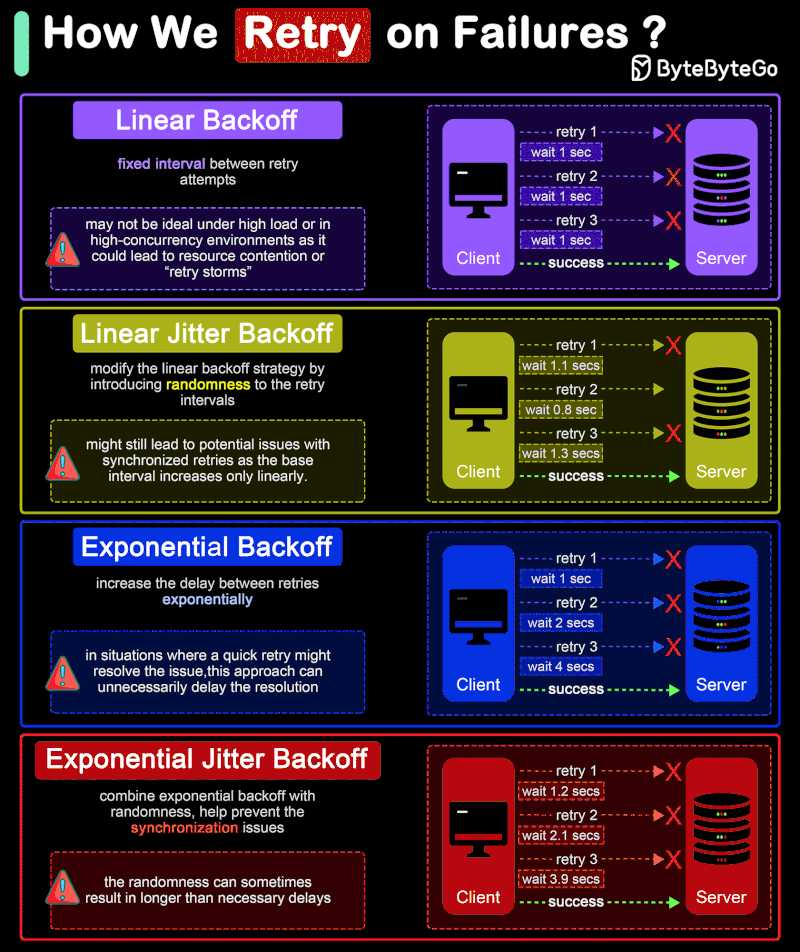
How do we retry on failures?
In distributed systems and networked applications, retry strategies are crucial for handling transient errors and network instability effectively. The diagram shows 4 common retry strategies.
🔹 Linear Backoff
Linear backoff involves waiting for a progressively increasing fixed interval between retry attempts.
Advantages: Simple to implement and understand.
Disadvantages: May not be ideal under high load or in high-concurrency environments as it could lead to resource contention or “retry storms”.
🔹 Linear Jitter Backoff
Linear jitter backoff modifies the linear backoff strategy by introducing randomness to the retry intervals. This strategy still increases the delay linearly but adds a random “jitter” to each interval.
Advantages: The randomness helps spread out the retry attempts over time, reducing the chance of synchronized retries across instances.
Disadvantages: Although better than simple linear backoff, this strategy might still lead to potential issues with synchronized retries as the base interval increases only linearly.
🔹 Exponential Backoff
Exponential backoff involves increasing the delay between retries exponentially. The interval might start at 1 second, then increase to 2 seconds, 4 seconds, 8 seconds, and so on, typically up to a maximum delay. This approach is more aggressive in spacing out retries than linear backoff.
Advantages: Significantly reduces the load on the system and the likelihood of collision or overlap in retry attempts, making it suitable for high-load environments.
Disadvantages: In situations where a quick retry might resolve the issue, this approach can unnecessarily delay the resolution.
🔹 Exponential Jitter Backoff
Exponential jitter backoff combines exponential backoff with randomness. After each retry, the backoff interval is exponentially increased, and then a random jitter is applied. The jitter can be either additive (adding a random amount to the exponential delay) or multiplicative (multiplying the exponential delay by a random factor).
Advantages: Offers all the benefits of exponential backoff, with the added advantage of reducing retry collisions even further due to the introduction of jitter.
Disadvantages: The randomness can sometimes result in longer than necessary delays, especially if the jitter is significant.